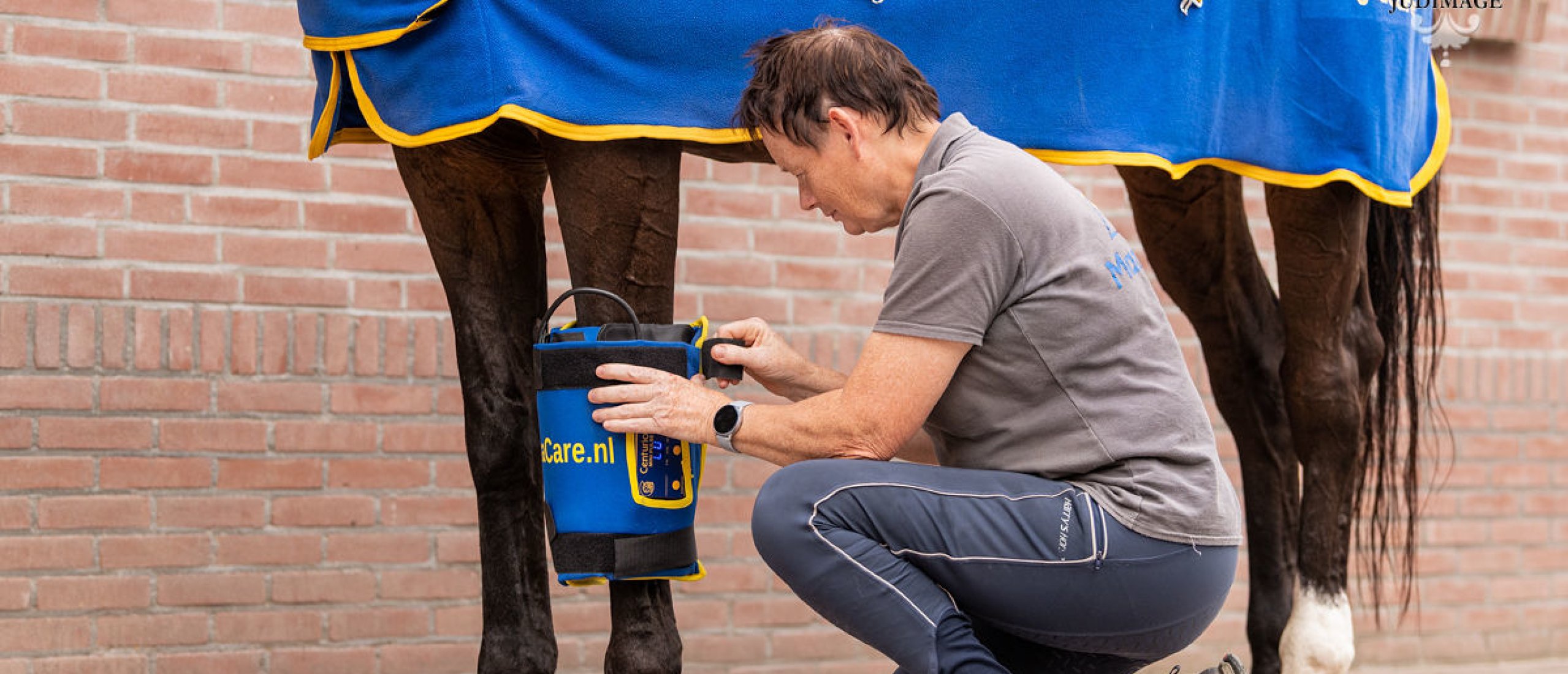
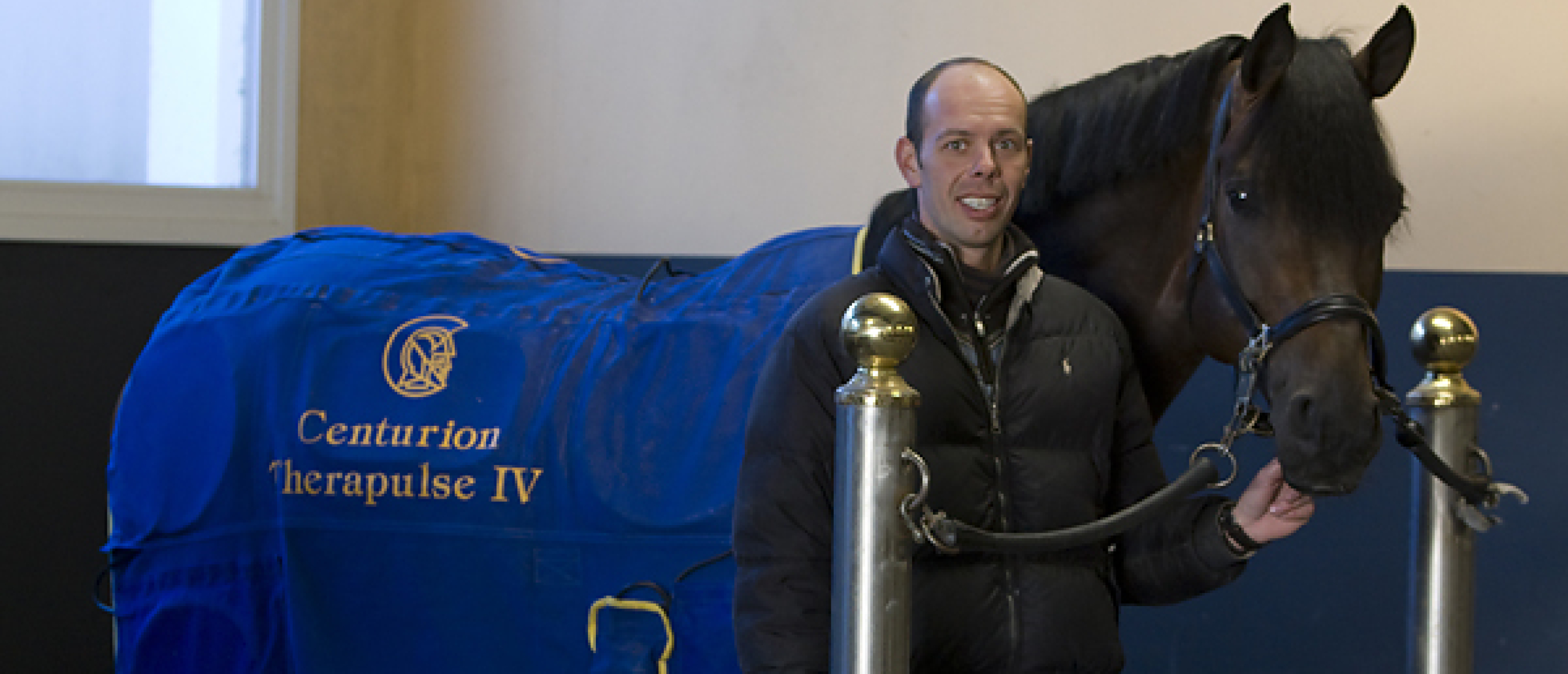
Laser therapy accelerate tissue repair
The most common example of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy is photosynthesis, where plants manufacture food from carbon dioxide and water. Light energy from the sun is the essential item in that process. No reasonable person disputes photosynthesis, it is a well know process that converts photons of light energy into chemical energy. The action of laser light is quite similar to photosynthesis in plants.
Photons of light from a laser, penetrate deeply into tissue and power the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is a molecule that is a major carrier of energy from one reaction site to another in all living cells. Increases in ATP as a result of laser light increases the energy available to the cell so that the cell can take in nutrients faster and get rid of waste products. In straight forward terms, the cells of tendons, ligaments and muscles are repaired faster as a result of exposure to laser light. How much faster? A good rule of thumb is that the time for healing is reduced by 2/3 ‘s of the time that it normally take with all other factors remaining the same, i.e. rest, nutrition, training.
Rapid Formation of Collagen
Collagen is the most common protein found in the body. It is estimated that 80% of the body is made up of this important fibrous protein. Various types of tissue make up the body. Connective tissue is the most widely distributed. In connective tissue, fibroblast cells produce the ground substance and tissue fiber. The “extra” energy from laser light is used by fibroblasts to increase collagen production. Collagen is the essential protein required to replace old tissue or to repair tissue injuries.
Perhaps the most common example of collagen is the clear sticky substance found around open wounds. Wounds are healed or closed over very rapidly by the application of laser light. There is also less scar tissue found when laser light is applied to the area.
Beneficial effect on nerve cells and the production of ß-endorphins
Laser light has a highly beneficial effect on nerve cells which blocks pain transmitted by these cells to the brain. Studies have shown that laser light increases the activity of the ATP dependent NA-K pump. In this case laser light increases the potential difference across the cell membrane moving the resting potential further from the firing threshold, thus, decreasing nerve ending sensitivity.
A less understood pain blocking mechanism involves the product of high levels of painkilling chemicals such as endorphins and enkephelins from the brain adrenal gland and other areas as a result of exposure to laser light.
Laser therapy accelerated lymphatic system activity and reduction in edema
Everyone wants to reduce swelling in a leg. The problem is that the veins in the leg are only capable of removing one component of the swelling. Blood vessels can remove the water but not the dirty protein solution that is present. So if you have a treatment modality that accelerates blood flow you have not solved this part of the problem. The lymphatic system is required to take away dirty proteins from edema. Laser studies conducted in 1987 and early 1988, indicate that laser light is capable of doubling the size of lymphatic ducts in the area of exposure and rapidly removing the protein waste.
Another important aspect of the study showed that laser light was capable of “perfect” regeneration of the lymphatic system in the immediate area with no leakage and no confused network of ducts. In the normal regeneration of lymphatic systems, the ducts are leaky and the duct network is complex and confusing , leading tot a tendency to have the same problem occur in the same area.
Formation of new capillaries and increased blood flow
Many types of treatments will increase blood flow. It has been shown that laser light does this extremely well, there is no question about that point. But what is not commonly recognized is that laser light will significantly increase the formation of new capillaries that speeds the healing process, closes wounds quickly and reduces scar tissue.